
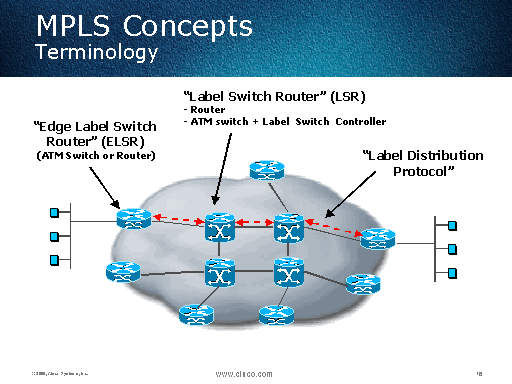
This is common in large service provider networks. A pure P router can operate without any customer/Internet routes at all. “P” stands for Provider Router and “PE” stands for Provider Edge Router Answer: “P” and “PE” are the terms which come from the description of VPN services. Question 1: What are the terms “P” and “PE”?. MPLS router roles may also be expressed as “P” or “PE”:. It is the key to scalable virtual private networks (VPNs) and end-to-end quality of service (QoS).įorwarding Equivalence Class (FEC) is a group of IP packets which are forwarded in the same manner (e.g., over the same path, with the same forwarding treatment)Ī label in MPLS is a short fixed length physically contiguous identifier which is used to identify a FEC, usually of local significance. MPLS can combine the intelligence and saleability of routing with the reliability and manageability of traditional carrier networks. It is the final router at the end of an LSP, which removes the label. It is also called Egress Node or Egress Router. Label Switching Router (“LSR”) or “transit node” is the router which only does MPLS switching in the middle of an LSP. LER is the router which makes the initial path selection. MPLS Router Roles/Positions: Label Edge Router (“LER”) or “ingress node” is the router which first encapsulates a packet inside an MPLS LSP. The LSP is required for any MPLS forwarding to occur. LSP is essentially a unidirectional tunnel between a pair of routers, routed across an MPLS network. MPLS Label Switched Path (“LSP”) is one of the most important concepts for the actual use of MPLS. MPLS sits between these traditional layers, providing additional features for the transport of data across the network. Layer 3 covers Internet-wide addressing and routing using IP protocols. Layer 2 covers protocols like Ethernet and SONET/SDH, which can carry IP packets, but only over simple LANs or point-to-point WANs. MPLS is best summarized as a “Layer 2.5 networking protocol”. MPLS stands for “Multi-Protocol Label Switching”. It provides an IP-compatible, QoS-capable infrastructure that enables the convergence of voice, IP, ATM, Ethernet, and Frame Relay onto the same backbone network. Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is one of the central elements of next generation networks. MPLS Training course provides an in-depth overview of MPLS technology, including MPLS theory, architecture, configuration, design issues, operations, troubleshooting, VPN, Traffic Engineering (TE), GMPLS (Generalized MPLS), MPLS-TP, and Seamless MPLS. 

Why should you choose TONEX for your MPLS Training? Space Operations and Cybersecurity Training.RF Engineering Training | Bootcamp Style.It is up to each student to obtain the simulator/emulator of their choice to study along with this course. The Cisco Packet Tracer and/or VIRAL (Virtual Internet Routing Lab) are Cisco proprietary softwares and can only be obtained through Cisco. It is the students responsibility to have these to practice with.
#MPLS FUNDAMENTALS COURSE HOW TO#
We will also learn how to create VRF's in order to make all this possible,Īs well as understand the CEF, LFIB, LRIB and much more tables in order toĭISCLAIMER: Please note that the simulators/emulators used in this course are not part of the course. We will definitely be creating Provider Edge routers Customer Edge RoutersĪnd have customers within the same company communicate with each other andĭifferent companies also be able to communicate with each other through VPN. Targets and Route Reflectors, we'll demonstrate how packets can be manipulated We will be creating multiple types of VPNs and through the use for Route Labels get forwarded and we will be configuring multiple IGP routing protocolsĪlong with BGP to get information across our network. Using the hands on lab we will get to see how these We will discuss the LDP protocol, what labels are and how they get forward We will beĭiscussing why MPLS was implemented, the terminology used in an MPLSĮnvironment, the configurations used in MPLS, concentrating in using Layer 3 In this course we will cover all the fundamentals of MPLS.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
